Designing for Equity
Collaborative Problem-Solving around Challenging Behaviors in Middle School
Topics

Together, educators are doing the reimagining and reinvention work necessary to make true educational equity possible. Student-centered learning advances equity when it values social and emotional growth alongside academic achievement, takes a cultural lens on strengths and competencies, and equips students with the power and skills to address injustice in their schools and communities.
Providing Agency for Our Most Challenging Students, Part 2
Teachers can employ Collaborative Problem Solving to empower students with persistently challenging behaviors to change.
In part one of this two-part series, we explored how the school-to-prison pipeline is an insidious problem that suggests that we need to be doing something differently to help students who exhibit persistent challenging behavior at school. At Two Rivers, we are using a collaborative problem solving model to help all students work with teachers to find solutions to this problem. The heart of the model is in empowering students to articulate their own perspective on potential problems and working with their teachers to come up with mutually acceptable solutions that address both underlying concerns on both sides.
Using the same five steps with students in Kindergarten through eighth grade, we’ve found that all students can start to take ownership of their challenges around empathy, relationship building, and collaboration.
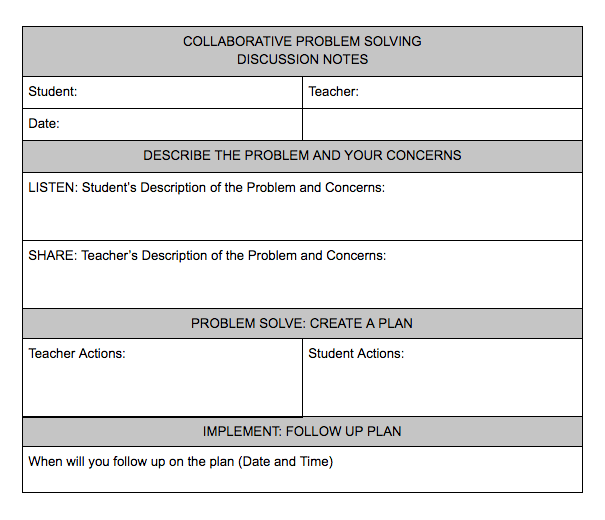
Once we as educators have identified a challenging behavior that we would need to work on with a student, the steps we use to solve the problem with the student is as follows:
- Listen: where we listen empathetically to hear the student’s concern about the persistent problem;
- Share: where we share our concerns about the persistent problem;
- Problem Solve: where we invite the student to come up with solutions with us that both address their concern and our concern and can realistically be implemented;
- Implement: where we put the plan into effect; and
- Reflect: where we evaluate the effectiveness of the plan with the student.
In the first post, Rachel Owens described how this can work in a Kindergarten classroom. Today’s story from Ama Teasdel explains what this looks like with students in middle school.
A Seventh Grade Example from Ama Teasdel
When we problem solve with students rather than for students, we empower them to take ownership of their learning. As a veteran special educator, I initially believed I was well versed in building relationships with students and working with them to address persistent challenging behavior. However, participating for two months in our school’s professional development training on collaborative problem solving conversations has proven me wrong. I’ve learned to become more humble and much more collaborative in my approach to problem-solving.
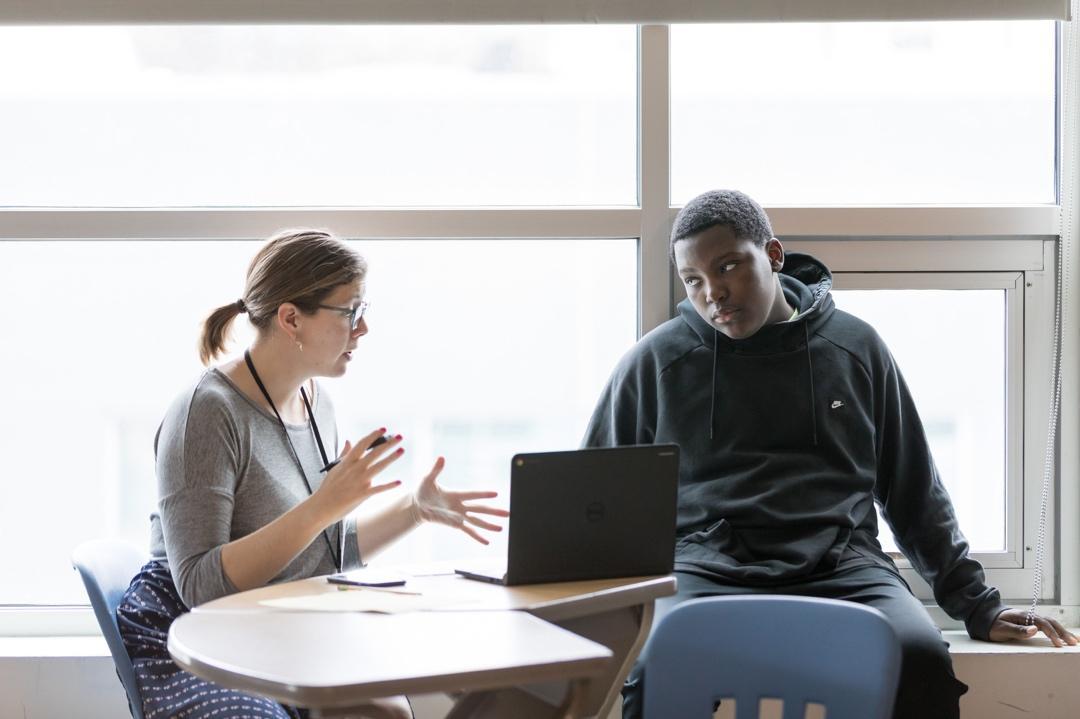

Henry, the first student I chose to engage in a collaborative problem solving conversation, is a student who has often been pegged as ‘unmotivated,’ or that he doesn’t care about school. I saw him as a hyperactive, disruptive, and disrespectful student who didn’t care about his academics and didn’t value what his classroom teachers, including myself, had to offer him. His classroom work completion was abysmal, and his negative behavior incidents caused him to lose anywhere from five to six instructional hours per week. Surprisingly, by opening up to collaboratively problem solve with a student, I learned three invaluable lessons from Henry.
Lesson One: Asking Before Assuming is at the Heart of Collaboration
I thought I had a generally positive rapport with Henry, so I believed that inviting him to the conversation wouldn’t be difficult. However, I was proven wrong. When I first approached him, he didn’t want to talk to me and he avoided having the conversation that I knew we needed to have. I assumed he wanted to avoid talking about a difficult topic. What I didn’t realize at the time was that I was asking him to join me for a conversation during lunch which was the only time he had to socialize with his friends. When I slowed down and asked him when a good time would be to meet, we identified a time right after he arrived to school so that he wouldn’t miss out on time spent with friends.
Lesson Two: Students’ Perceptions are Their Reality, and Successful Solutions Must Take Their Perspectives Into Account.
Once we were able to have the initial conversation, I sat with Henry in a time and space of his choosing and really listened to him. I went in thinking that I already knew what Henry’s issues were. To be collaborative, I had to be humble and realize that I needed to hear from my students to truly understand their concerns. What I learned was that Henry had a lot of adult responsibilities caring for siblings before school. This impacted his ability to focus and stay on task. In addition, he shared that he wanted to do well, but as he said “I think they (teachers) don’t like me because they always say bad stuff to me and tell me what I am doing wrong.” He felt that any time an adult approached him that they would always have something negative to say. From my perspective this was an over-generalization; however, I had to humble myself and seek to understand the truth in what Henry was saying.
Lesson Three: Share Concerns in a Variety of Ways and Invite Students to Help Define Concerns with You.
Once I had actually taken the time to listen without using preconceived notions as a barrier, I had a better, albeit not perfect, understanding of Henry. This enabled me to take the next step of sharing my perspective. I shared with Henry that I had seen him in the hallways a lot when he was supposed to be in class; that his off-task behaviors in class distracted others; and that when he is redirected, his response is not the most appropriate. As I was sharing with him, it was clear from his body language that he was tuning me out. Thinking about what he had just shared with me, I realized that he was likely feeling overwhelmed by all the negative things I was sharing and I was feeding the perception that teachers only had negative things to say to him. So, I invited him in to think about how he responds to redirection, and that we could revisit that later.
Based on my conversations with Henry, my mindset and practices have shifted. I no longer take my experience for granted. Each student is a different and dynamic person. Even with 15 years of experience as a special educator, I still need to hear and understand the daily experiences and realities of my seventh graders. Problem solving does not only center around a problem I have defined, but the ways that we define the problem together. The beauty of collaborative problem solving conversations is that they empower both the student and teacher to define what success means. By giving middle school students autonomy to define and solve those problems collaboratively with their teachers, they take ownership and transfer critical skills.
Within the past few weeks, Henry’s negative incidents have decreased, and he is completing more classwork. Yes, he is still coming into class sleepy, hungry and sometimes ‘irritable.’ However, we are all equipped with a better understanding and tools to combat his challenges. We as staff are more cognizant of our interactions with him to make sure we are highlighting the positive with every chance we get. Just being aware of how we perceive his responses, Henry has also accepted redirection by responding in a more positive way and following directions and advocating for himself.
Using collaborative problem solving to address challenging behaviors has not only improved student behavior, but it has improved staff and student relationships while also building essential skills to help students take ownership of their learning.
Providing Agency for Our Most Challenging Students
As the two examples in this and in the previous post highlight, we have discovered that providing opportunities for students in Kindergarten through middle school to share their concerns and to collaboratively approach ways to overcome challenges with a teacher empowers them to be their best selves. They are learning the life skills of empathy, collaboration, and problem solving. Building these skills in the safe environment of schools with caring adults equips all of our students to better navigate challenges in their lives outside of school and on into adulthood. As a result, we are working to break the school-to-prison pipeline.
Read Part 1 of Providing Agency for Our Most Challenging Students: Collaborative Problem Solving around Challenging Behaviors in Kindergarten.
For more about Collaborative Problem Solving, read the related article, Connections over Consequences: Effective Strategies for Collaborative Problem-Solving with Students.