Gooru
Tools, digital content, and data for students to own their learning. ...

Educators often take advantage of educational technologies as they make the shifts in instruction, teacher roles, and learning experiences that next gen learning requires. Technology should not lead the design of learning, but when educators use it to personalize and enrich learning, it has the potential to accelerate mastery of critical content and skills by all students.
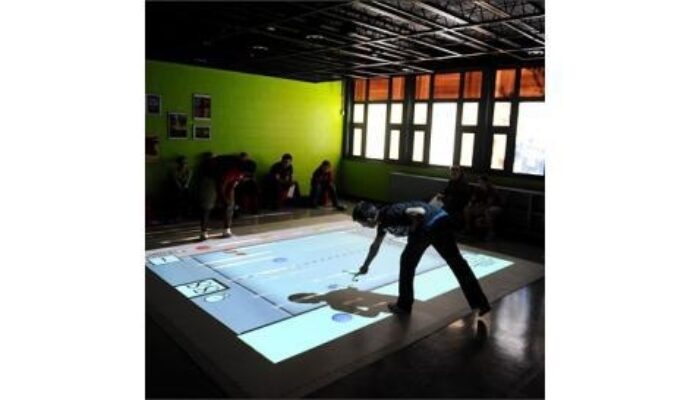
Embodied learning (think Xbox Kinect) literally connects students’ actions to learning, making the classroom experience more engaging and interesting. For example, motion-capture technology tracks students’ 3D movements in an immersive, interactive space.
As students learn about a physics concept like velocity, they can hear the sound of their actions getting faster. They can see graphs and equations that represent their motions in real time. They can feel the weight of an object in their hand as they interact in real physical space. Their physical gestures help them to understand the content in a deeper manner.
SMALLab Learning creates embodied learning environments that integrate new technologies and contemporary research from the learning sciences. For example:
Common Core State Standards: All content aligns with Common Core Math Standards and National Science Standards.
Introduction to SMALLab Learning
Research shows SMALLab’s positive impact on student learning when compared to regular classroom instruction.
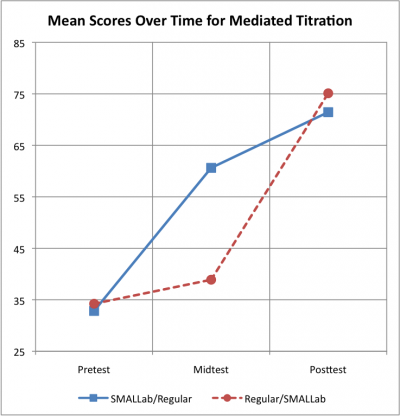
Multiple classes in an urban high school randomly received either SMALLab or regular instruction first. Students took the mid-test and then the order of intervention switched. Students took the content test three times—pretest, mid-test and post-test—during the six-day study.
Videotaped learning sessions showed substantially higher student-driven utterances in SMALLab when compared to the same students learning with their teacher in their regular classroom. The videotapes noted a marked increase in the number of student-to-student and student-to-teacher discussions during SMALLab.
Pre-, mid-, and post-test results are shown in this graph:
SMALLab and partner Arizona State University used NGLC funding to deliver a set of seven embodied learning scenarios and an eight-day curriculum to two schools. The team trained four teachers how to use the scenarios and approximately 220 students participated in the pilot.
Since the project, SMALLab commercialized several enhanced learning scenarios and an embodied learning environment, available at the SMALLabLearning website.
Long Term Goal: To demonstrate how SMALLab can invigorate learning about simple machines as a means to ultimately improve graduation rates and encourage greater interest in math and science careers.